When constructing a solid foundation for any structure, the role of plinth beams cannot be overstated. It is also known as a tie beam and plays a crucial role in maintaining the stability and durability of a building. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of plinth beams, which new civil engineers, enthusiastic homeowners, and contractors can learn its importance for the construction of buildings. We will explore the importance of plinth beams and their contribution to building stability, exploring various aspects that make them an integral part of construction projects.
What is a Plinth Beam?
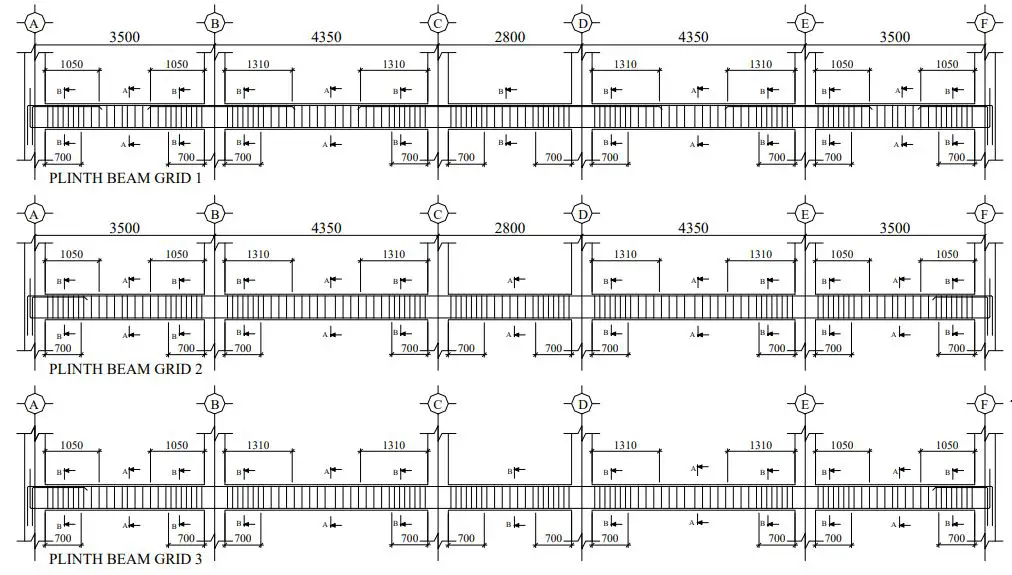
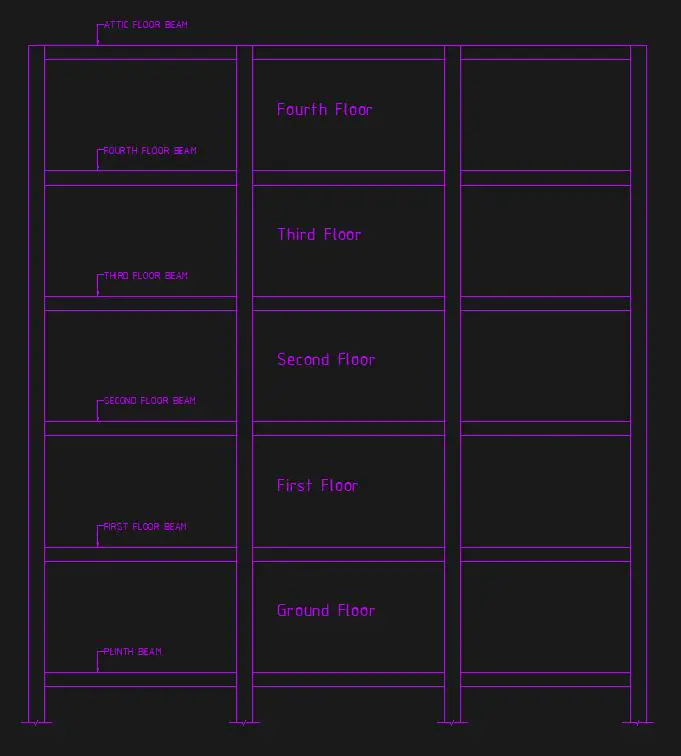
A plinth beam (PB) is a reinforced concrete beam above the foundation and under the wall in a framed structure, placed at or above ground level, that supports the load of the wall above. PB acts as a horizontal support system in a building, connecting and reinforcing the walls at the ground level. They are specially constructed in areas prone to earthquakes. The primary purpose is to distribute the structure’s load uniformly, thereby reducing the impact of settlement and preventing structural failures.
In the case of load-bearing masonry structures, it is constructed as a plinth band which has a similar facility to that of a plinth beam.
Also, read: 4 Types Of Seismic Bands For Masonry Structure | Horizontal Bands| Advantages And Disadvantages
Location and Application
- The plinth beam holds the lowest position in the hierarchy among the various beams within a building’s structure if the strap beam and ground floor beam are not taken into consideration.
- Plinth beams are typically constructed at the ground level, within the plinth height of a building.
- Both load-bearing masonry structures and frame structures are provided with tie beams in earthquake-prone areas to uphold the integrity of the buildings.
The Significance of Plinth Beams
- Load Distribution:
- It efficiently distributes the load from the walls to the foundation, ensuring that the weight is evenly transferred.
- Preventing excessive settlement enhances the structural stability and integrity of the building.
- Resistance to Earthquakes and Vibrations:
- It plays a vital role in mitigating the effects of seismic activities and vibrations.
- Their interconnected nature strengthens the overall structure, reducing the chances of structural damage during earthquakes and vibrations.
- Protection Against Soil Moisture:
- It acts as a barrier between the structure and the ground, safeguarding the walls against soil moisture and dampness.
- This prevents moisture-related issues such as seepage, mould growth, and damage to the structural elements.
- Counteracting Lateral Forces:
- It provides lateral support to the walls, helping to counteract the forces caused by wind pressure, soil pressure, and other external factors.
- This reinforcement enhances the building’s ability to withstand these forces and reduces the risk of structural failure.
Also, read: Types Of RCC Beam
Design and Construction Considerations
- Structural Design:
- The design of PB should be carried out by qualified structural engineers to ensure optimal dimensions, reinforcement, and placement.
- The minimum thickness of the plinth beam is usually 150mm (6 inches) for the masonry structure and 200mm (8 inches) for the R.C. frame structure. The width is constructed to match the width of the wall course.
- Factors such as building height, soil conditions, and the anticipated loads need to be considered during the design process.
- Material Selection:
- The use of appropriate materials (mixed design concrete) enhances the resistance of the plinth beam against environmental factors and ensures long-term durability.
- The minimum strength of concrete is M20 or M25 is used for the construction of plinth beams according to IS 19320-2016. Compressive strength of 25 Mpa and more is usually provided to the building with 10m height.
- Corrosion-resistant steel reinforcement and deformed bars such as TMT and TMX should be used to ensure the longevity and strength of PB.
- Nominal reinforcement of 12ø and 10ø is provided as bottom and top reinforcement with shear stirrups spaced at 150 millimetres from centre to centre.
- Construction Techniques:
- Proper construction techniques, including formwork, compaction, and curing, should be employed during the construction of any reinforced concrete work considering the plinth beam.
- Adequate supervision and quality control measures are essential to ensure the beams are constructed in accordance with the approved design.
plinth beam reinforcement
The reinforcement for a plinth beam, like any other structural element, depends on factors such as the span of the beam, the loads it will carry, and the structural requirements of the building. Plinth beams are typically designed to provide lateral stability to the structure and distribute loads from the walls to the foundation. The reinforcement in a plinth beam is mainly in the form of steel bars and deformed bars such as TMT and TMX.
Also, read: Which is better: TMT And TMX Steel reinforcement bar?
Conclusion
Plinth beams are the unsung heroes of building stability, providing essential support and reinforcement to structures. Their significance in distributing loads, resisting seismic forces, protecting against moisture, and countering lateral pressures cannot be overlooked. For new civil engineers, enthusiastic homeowners, and contractors, understanding the importance of plinth beams is crucial in ensuring the durability and safety of any construction project. By adhering to proper design, construction, and maintenance practices, we can harness the full potential of plinth beams and build structures that stand the test of time.
Also, read: Column Failure: Causes | Types | Prevention
FAQs:
Q: What is Plinth Beam?
Ans: A plinth beam is a reinforced concrete beam located above the foundation and below the wall in a framed structure. It is strategically positioned at or slightly above ground level to provide essential support for the wall above it. Serving as a horizontal support system, it plays a vital role in connecting and reinforcing the walls at the ground level. They are particularly significant in regions prone to earthquakes, where their construction becomes even more crucial. The primary objective is to distribute the load of the structure uniformly, effectively minimizing settlement effects and preventing any potential structural failures.
Q: What is the purpose of the plinth beam?
Ans: The purpose of the plinth beam is as:
1. Load Distribution: One of the primary purposes of a plinth beam is to distribute the load from the walls to the foundation. Providing a horizontal support system, it helps to transfer the weight of the walls and other superimposed loads to the foundation in a uniform manner. This helps to prevent excessive settlement and ensures the structural stability of the building.
2. Structural Stability: The PB contributes significantly to the overall stability of the structure. It acts as a horizontal tie between the walls at the ground level, connecting and reinforcing them. This helps to enhance the rigidity and resistance of the building against lateral forces, such as wind pressure and seismic activity, thereby reducing the risk of structural failure.
3. Earthquake Resistance: In areas prone to earthquakes, PB plays a crucial role in enhancing the seismic resistance of the structure. By providing additional reinforcement and connectivity between the walls, plinth beams help to distribute the seismic forces and minimize damage during an earthquake. They help to maintain the integrity of the building and protect it from potential collapse.
4. Protection Against Moisture: PB acts as a barrier between the structure and the ground, safeguarding the walls from moisture and dampness. They help to prevent the ingress of water from the soil, which can lead to issues such as seepage, damp walls, and deterioration of the structure. By protecting against moisture, PB contributes to the longevity and durability of the building.
5. Mitigating Differential Settlement: Differential settlement refers to the uneven settlement of different parts of a building’s foundation. PB helps to reduce the impact of differential settlement by providing a level and uniform base for the walls. This helps to minimize cracks and structural damage that can occur due to uneven settlement, ensuring the overall stability and integrity of the structure.
Q: What is the size of the plinth beam?
Ans: The minimum thickness of a plinth beam can vary depending on several factors, such as the design requirements, the load-bearing capacity needed, and the structural conditions. However, as a general guideline, the minimum thickness of aPB is typically around 150 to 200 millimetres (6 to 8 inches).
Q: What should be the reinforcement for the plinth beam?
Ans: The reinforcement for the plinth beam should be properly designed. However, a nominal reinforcement bar of 10ø and 12ø are provided as top and bottom rebar and shear stirrups are provided at 150mm centre to centre.
References:
- Bhavikatti, S. S. (2010). Basic civil engineering. IK International Publishing House Pvt. Ltd.
- Housing News. (2023). Plinth beam: Meaning, size, requirements, materials and significance. Housing News. https://housing.com/news/plinth-beam/
- Hamakareem, M. I. (2021). What is a Plinth Beam? Its purpose, Applications and Construction: Explained With Video. The Constructor. https://theconstructor.org/structural-engg/plinth-beam-purpose-applications/20892/
![]()