In steel construction, bolt holes play a crucial role in ensuring the structural integrity and stability of the assembled components. These holes are strategically placed to accommodate bolts that secure different steel members, connecting them into a cohesive and robust structure. The precision and design of bolt holes are paramount to the overall strength and safety of the structure.
Types of Bolt Holes
The type of holes used for bolted connections depends on the specific requirements of the design and the type of connection being used. Here are some common types of holes for bolted connections:
- Through holes
- Slotted holes
- Oversized holes
- Tapped holes
- Blind holes
1. Through Holes/Clear Holes (STD):
These holes go completely through the connected elements, allowing the bolt to pass through. This is the most common type of hole for bolted connections.
2. Slotted holes (SSL)
These are elongated holes that allow for some adjustment during assembly. Slotted holes are useful when there might be slight misalignments in the position of the connected elements. There are two types of slotted holes, namely short slotted holes and long slotted holes.
- Short Slotted Hole
Short-slotted holes are permitted in any or all plies of slip-critical or bearing-type connections. The slots are permitted without regard to the direction of loading in slip-critical connections, but the length shall be normal to the direction of the loading in bearing-type connections.
- Long Slotte Hole
Long-slotted holes are permitted in only one of the connected parts of a slip-critical or bearing-type connection at an individual faying surface. Long-slotted holes are permitted without regard to the direction of loading in slip-critical connections but shall be normal to the direction of loading in bearing-type connections
3. Oversized holes (OVS)
Oversized holes are larger in diameter than the bolt diameter. They provide additional clearance for the bolt, allowing for some flexibility during assembly. These holes are acceptable in one or multiple layers of slip-critical connections; however, they must not be employed in connections of the bearing type.
Also, read: What Is Structural Steels? | Types | Usage
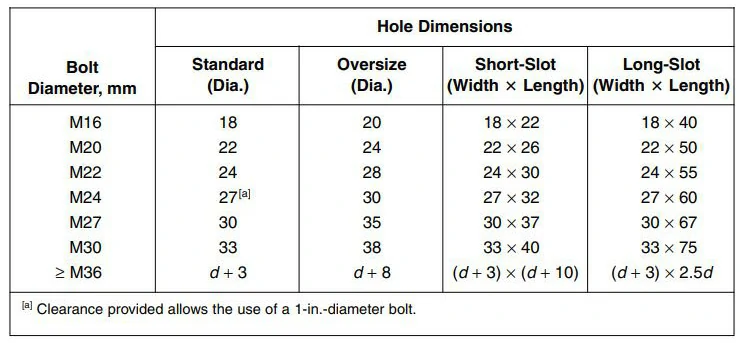
Other types of bolt holes that are used less frequently, such as:
- Tapped holes: These holes are threaded and are used for bolts that screw directly into the steel.
- Blind holes: These holes do not go all the way through the steel member and are used for connections that need to be hidden from view.
Also, read: Comprehensive Guide To Tension Members In Steel Structure 101
Specification For Bolt Holes
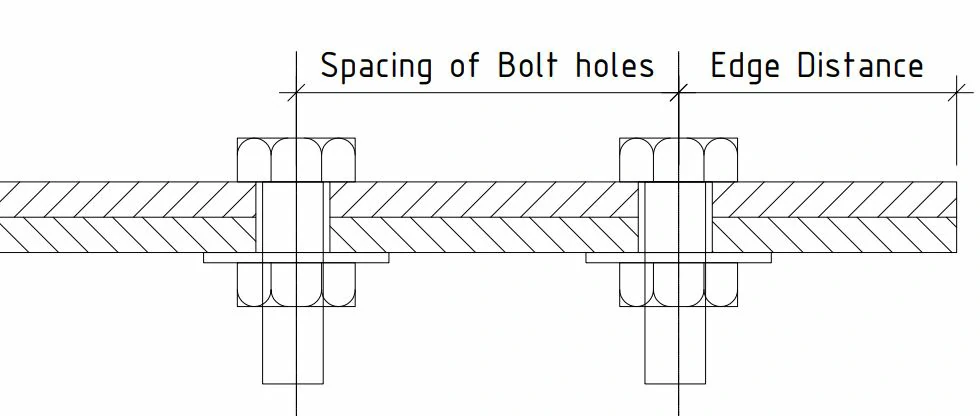
Minimum Spacing of Bolt holes
The American Institute of Steel Construction (AISC) provides guidelines for the minimum spacing of bolt holes in steel structures. The minimum spacing is essential to ensure the structural integrity and proper performance of bolted connections. The specific requirements can vary depending on the type of connection and loading conditions. However, in general, the AISC provides guidelines for the minimum edge distance and end distance for bolt holes.
The distance between the centres of standard, oversized, or slotted holes should be at least 2 2/3 times the nominal diameter, denoted as “d,” of the fastener. The clear distance between bolt holes or slots (the unobstructed space between them) should not be less than the nominal diameter “d.”
According to AISC, While the minimum requirement is stated, there is a user note suggesting that a distance between the centres of standard, oversized, or slotted holes equal to 3 times the nominal diameter “d” (3d) is preferred. This indicates that, for optimal performance and safety, a greater distance between hole centres is recommended. This preference might be based on considerations such as ease of fabrication, assembly tolerances, or specific structural design requirements.
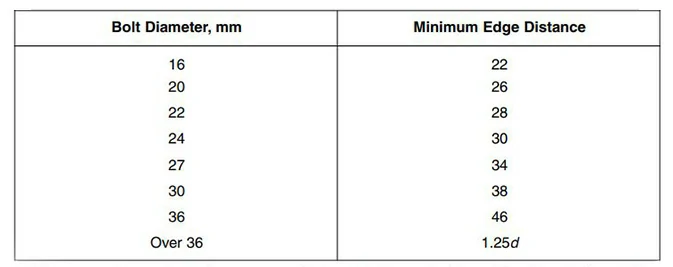
Minimum Edge Distance of Bolt holes
The minimum edge distance is the distance from the centre of a bolt hole to the nearest edge of the connected member. AISC typically provides specific values for minimum edge distances for a standard hole
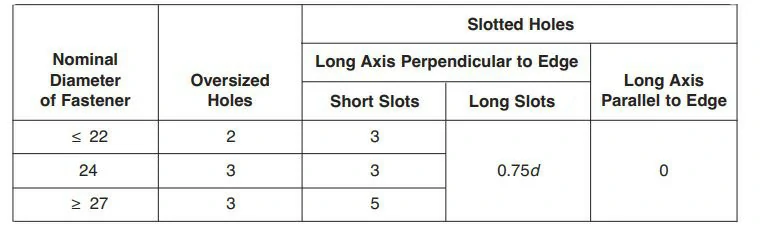
Maximum Edge Distance of Bolt holes
The distance from the centre of any bolt to the closest edge of parts in contact should not exceed 12 times the thickness of the connected part being considered, with a maximum limit of 150 mm (6 inches). Regarding the longitudinal spacing of fasteners between elements involving a plate and a shape, or two plates in continuous contact, the specifications are as follows:
- In the case of painted members or unpainted members not susceptible to corrosion, the spacing should not exceed 24 times the thickness of the thinner part or 300 mm (12 inches).
- For unpainted members made of weathering steel and prone to atmospheric corrosion, the spacing should not exceed 14 times the thickness of the thinner part or 180 mm (7 inches).
Also, read: Advantages And Disadvantages Of Welded Joints
FAQs:
Q: What are the different types of holes in structural steel?
Ans: In steel structures, according to the American Institute of Steel Construction (AISC), there are three main types of bolt holes:
1. Through holes (STD): These are the most common type of hole and are simply round holes that the bolt passes through. They are used for static connections where the bolt does not need to move.
2. Slotted holes (SSL): These holes are oval-shaped and allow the bolt to move slightly in one direction. This is useful for connections that need to accommodate thermal expansion or movement due to wind or earthquakes.
2. Oversized holes (OVS): These holes are larger than the diameter of the bolt and are used for connections that require high bolt tension. The larger hole allows the nut to be tightened more, which creates a stronger connection.
Q: Which bolt hole is used for the column base plate?
Ans: The two primary types of bolt holes commonly used for column base plates are:
Slotted Holes (SLO):
Slotted holes provide more flexibility in adjusting the position of the column during erection. They allow for some lateral movement of the column, which can be useful when aligning multiple columns or accommodating construction tolerances. Slotted holes are often used in situations where precise alignment is critical.
Standard Holes (STD):
Standard holes are typically used when high precision in the alignment of the connected parts is not critical. These holes are larger than the nominal bolt diameter, allowing for some tolerance in the alignment during construction. Standard holes are often used in cases where the column’s position can be adjusted slightly during the erection process.
References:
- 5.1. Bolt Holes | American Institute of Steel Construction. (n.d.). https://www.aisc.org/steel-solutions-center/engineering-faqs/5.1.-bolt-holes/
![]()