Have you ever considered having an insulated home with a decorative exterior wall? Did you ever think of constructing such a kind of home which is economical? Here is one of your choice of home: Read about the cavity wall.
What is a Cavity Wall?
A cavity wall is a wall constructed with an air space called a cavity of width varying from 4cm to 10cm between the inner and outer brick or block leaves. The inner and outer section of the wall separated by air space is called leaves. The inner leaf and outer leaf of the wall are tied together by wall ties which are spaced 0.3m apart in the horizontal course and 0.3 to 0.45m in vertical alignment.
These walls have better thermal insulation and weather-resistance properties compared to ordinary solid brick or block walls. It is also known to prevent the entry of dampness and acts as sound insulation. They are generally built as enclosures of residential buildings.
The minimum thickness requirement of each leaf is generally 90mm with a 50mm cavity. However, different countries have their specification stipulated in the Building guidelines.
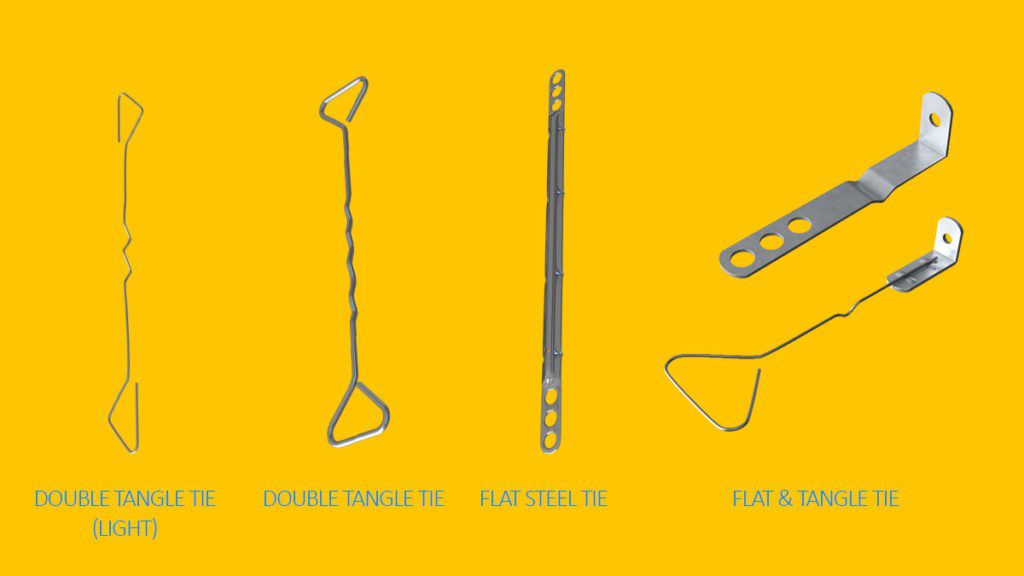
Purpose of Cavity Walls
Cavity walls are determined to have the following purposes: –
Thermal Insulation
The air space between the inner and outer leaves acts as insulation or is resistant to the transfer of heat. It helps in preventing heat loss during the cold seasons, from the inner leaf to the outer wall. During hot seasons, the outer heat is not conducted to the inner leaf which makes the rooms remain cool inside.
Damp Prevention
Although the exterior wall is constantly exposed to natural elements and moisture, the cavity provided will reduce the entry or infuse of moisture to the inner leaf of the wall. Thus, acting as damp prevention for the home in highly humid areas.
Sound Insulation
The air space and the insulation materials filled in the cavity help in sound insulation. The large quantity of noise from the outer environment is absorbed by the air space provided in the cavity walls.
Economical Construction
The construction of a cavity wall is economical to other types of walls. However, the cost of the wall depends upon the availability of the materials. The finding by W.B. McKey in his book Building Construction, it was stated that building a 275 mm cavity wall costs less than constructing a 328 mm solid wall
Efflorescence Prevention
Due to the cavity, the moister is prevented from passing through the wall and the formation of effluent on the brick wall is prevented.
Types of Cavity Wall
Stone Cavity Wall
When the stone is abundantly available and is the material for construction in the locality, dressed stone cavity walls are constructed. The width of the stone is 150 to 225mm is used for the outer leaf of the wall. A lightweight concrete block is used in the inner leaf of the cavity wall, to give the stability of the wall ties provided at the distance mentioned above.
Brick Cavity Walls
Usually in this type of wall, the outer and inner leaves are constructed with brick masonry with the pointing in the outer leaf. The insulation materials are pumped in through the temporary opening provided at mortar joints. The inner and outer leaf is connected with wall ties.
Also, read: Types of Bricks Used in Building Construction | 6 Types of Bricks
Insulation Materials for Cavity Walls
The most common types of cavity wall insulation used are: –
Mineral Wool/Mineral Fibre or Rockwool
Brown mineral wool is one of the common types of insulation material used for insulation in residential buildings. Brown mineral fiber consists of stands of fiberglass or mineral wool made from an igneous rock which is heated and spun to create fiber material. Mineral wool or fibre is forced into the cavity using compressed air.

Polystyrene Beads or Granules
Polystyrene beads are an insulation material which is generally used in narrower cavity walls. They are available in loose or in a light sticky resin. Polystyrene granules and beads are blown into the cavity with compressed air.
Urea Formaldehyde Foam
Is created within the cavity walls by injecting and simultaneously mixing two chemical components to form a foam which will fill the cavity.
Also, read: 10 Effective Thermal Insulation Materials for Building
Construction of Cavity Wall
Sub-Structure
The construction of cavity walls is the same as other load-bearing construction. The foundation for the cavity wall is constructed similarly to other load-bearing structures. No footing is required; just a plain concrete base is adequate for the foundation works and such is provided to the load-bearing structure. However, the cavity between the inner and outer leaves is filled with lean concrete as suggested by Building regulations of the region. The whole of the construction project and proper supervision should be considered during the construction.
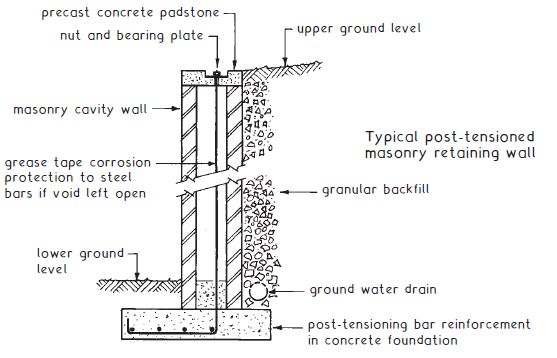
Super-Structure
The superstructure wall should be constructed with chosen materials. Wall ties should be provided to connect the inner leaf and outer leaf. Horizontal spacing between ties is 750mm minimum and a maximum of 900mm. The vertical spacing is 300mm to 450mm. The cavity in the superstructure is either left empty or filled with insulation materials.
The weep holes are provided for the outer leaf at the bottom with an interval of 1 m.
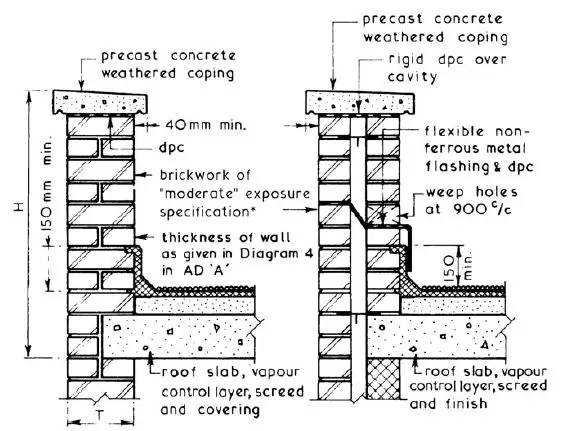
Parapet walls need to be covered with concrete coping in order to prevent the entry of moisture,
Damp Proofing for Cavity Wall
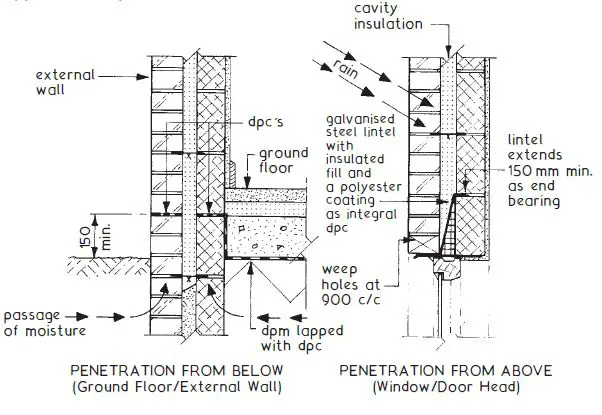
Dampproofing for the cavity walls is very important as it could lead to damage to walls. Damp proofing membrane shall be laid under the floor on the ground floor. The window and door jams shall be provided with necessary damp proofing as shown in the figure below.
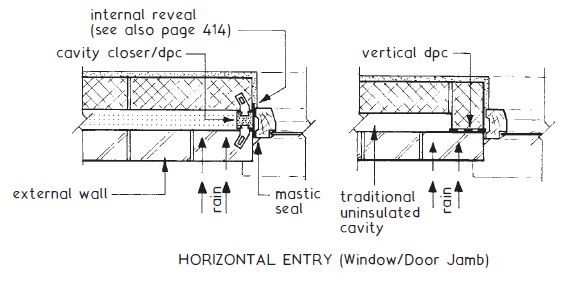
Advantages.
- As the inner and outer leaf of the wall is disconnected the moisture (dampness) cannot travel inside the building or outside the building, Thus reducing the chance of efflorescence.
- The cavity between the two leaves is full of air which is a bad conductor of heat. Hence transmission of heat from the external face to the inside the room is very much reduced. Cavity walls have about 25% greater insulating value than the solid walls.
- Cavity walls are very good insulation against sound technology.
- They are cheaper and more economical
- Loads on foundations are reduced because of lesser solid thickness
Disadvantages.
- Wall ties tend to corrode.
- Requires good supervision during its construction phase.
- It demands skilled labour, masons and experienced designers.
- It requires the installation of a vertical damp proof course at different levels of wall opening and enclosure (plinth level, parapet wall, etc.).
Also, read: Types of Door Frames: Size, Materials & Specification
FAQs:
-
Q: What is a cavity wall?
Ans: A cavity wall is constructed with an air space called a cavity of width varying from 40mm to 100mm between the inner and outer section of brick or block. These inner and outer walls are separated by air space called leaves and are filled with insulating materials. The inner leaf and outer leaf of the wall are tied together by wall ties which are spaced 0.3m apart in the horizontal course and 0.3 to 0.45m in vertical alignment.
-
Q: Where are cavity walls used?
Ans: Cavity walls are constructed in colder regions because of their good properties of thermal insulation. They can also be built where sound insulation is needed.
-
Q: Why are wall ties used in cavity walls?
Ans: Wall ties are provided in the cavity wall to hold the two leaves together. The ties used for the purpose should be sufficiently strong, non-corrodible and should be so shaped that water entering through the outer leaf does not travel along it. These ties must be placed at a distance of 900 mm maximum horizontally and 450 mm vertically. Ties are usually made of mild steel.
Reference: –
- Chundley Roy and Greeno Roger (2014), Building Construction Handbook, Prentice Hall, Tenth edition
- Mehta Madan, S. Walter & Armpriest Diane (2009), Building Construction, Principles, Materials, and Systems, Update
- Dr. B.C. Punmia (2006), Building Construction, Laxmi Publication (P) LTD
![]()







