Columns are important structural elements that provide support for buildings, bridges, and other structures. However, they can fail due to various reasons, leading to catastrophic consequences. In this article, we will discuss the causes and types of column failures, as well as ways to prevent them.
Causes of Column Failure:
Failure of the column can be caused by one or more factors. Some of the causes can be as follows:
Excessive Load: One of the main reasons for column failure is the application of excessive loads on the column. When the applied load exceeds the design load of the column, it can cause the column to buckle, crush, or fail in shear.
Poor Design: A poorly designed column can also lead to premature failure. The design must take into account the loads the column will be subjected to, the material properties, and the column’s dimensions.
Material Defects: The presence of material defects such as cracks, voids, or inclusions in the column material can weaken the column, making it susceptible to failure.
Corrosion: In the case of steel columns, exposure to corrosive environments can weaken the column material, leading to corrosion of steel and eventually failure. If the concrete reinforcement column is also exposed to a corrosive environment or has not provided adequate nominal cover, the reinforcement can get corrosion weakening the column’s strength.
Fatigue: Repeated loading and unloading cycles can cause the material to weaken and eventually fail. This is known as fatigue failure.
Construction Errors: Construction errors usually occur when the construction work deviates from the structural design and drawing. Errors made during the construction process such as incorrect alignment, poor welding, or improper placement of reinforcing bars can lead to column failure.
Foundation Failure: A weak or inadequate foundation design can cause the column to settle, tilt or even collapse.
Types of Column Failure:
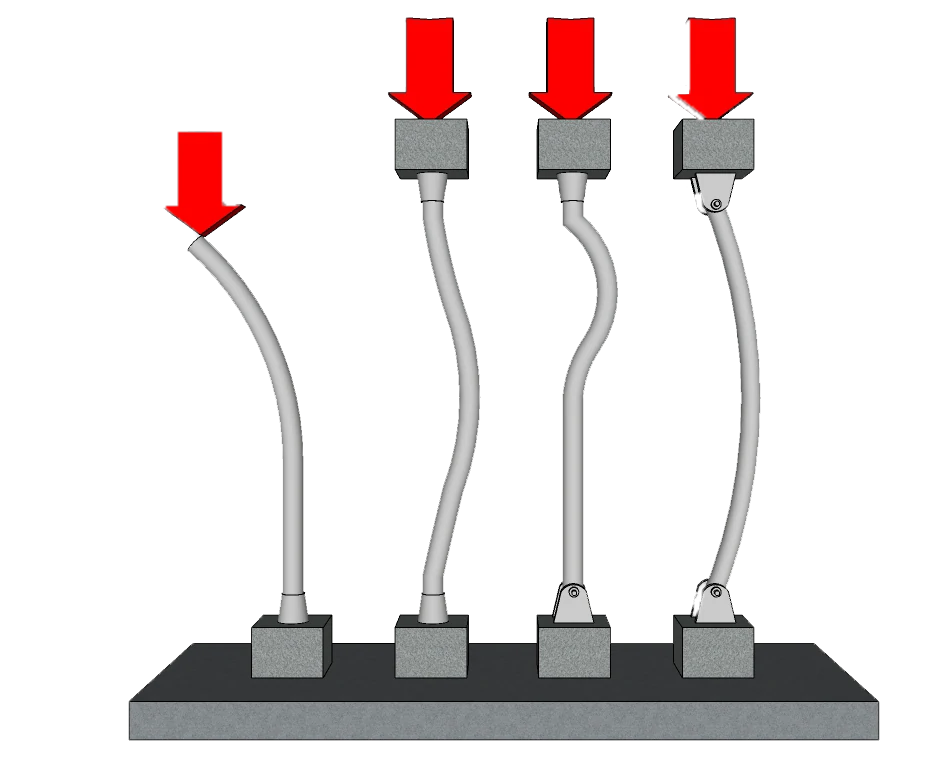
Buckling Failure:
Buckling failure is a type of column failure that occurs when the column is subjected to compressive loads that cause it to suddenly bend or buckle, leading to collapse. Buckling failure is commonly observed in slender columns due to elastic or plastic instability, or with a high aspect ratio, such as those found in tall buildings and structures.
Buckling failure occurs when the compressive load exceeds the critical buckling load, which is the maximum load that the column can sustain without buckling. The critical buckling load depends on various factors, including the material properties, the cross-sectional area, and the length of the column.
As per Cl. 26.5.3.2 of IS 415: 2000, transverse or helical reinforcement in the form of polygonal links (lateral ties) or circumferential tension is provided to give effective lateral support against buckling in the column.
Also, read: Slenderness Ratio Of Compression Members: Effective Length and Radius of Gyration
Compression Failure in The Column
Compression failure in a column occurs when the column is subjected to compressive loads that exceed its capacity to withstand such loads, leading to a sudden failure. Compression failure is usually observed in short columns or those with a large cross-sectional area.
Compression failure in columns can be caused by various factors, including inadequate column design, insufficient material strength, overloading, and instability due to lateral loads or wind loads.

Also, read: Types of Loads on Building Design
Crushing Failure:
This occurs when the column material is unable to withstand the compressive loads and the column crushes or deforms permanently. This type of failure usually occurs in short and stubby columns.
Shear Failure:
Shear failure in a column occurs when the material (concrete) of the column is unable to resist the shear stress applied to it, resulting in a sudden failure. Shear stress occurs when forces are applied parallel to the cross-sectional area of the column, causing it to slide or shear apart. Shear failure usually occurs in tall and slender columns, where the load is not uniformly distributed across the cross-section.

Fatigue Failure:
This failure is a type of column failure that occurs when a column is subjected to repeated loading and unloading cycles over an extended period of time. This can cause the material to weaken and crack, eventually leading to failure. Fatigue failure is commonly observed in structural components that experience cyclic loading, such as bridges, overhead water tanks, aircraft, and high-rise buildings.
Corrosion Failure:
This occurs when the column material is exposed to corrosive environments, such as saltwater, chemicals, or acidic solutions, which weaken the material and eventually cause the column to fail.
Overloading Failure:
This occurs when the column is subjected to loads that exceed its capacity, leading to permanent deformation or collapse.
Foundation Failure:
This occurs when the column’s foundation is unable to support the column’s weight or the loads applied to the column. This can lead to settlement, tilting, or even collapse of the column.
Also, read: Compressive Strength Of Concrete
Prevention of Column Failure:
Failure of the column can be prevented by following the points listed below:
- Proper Design: Proper column design, taking into account the loads, material properties, and dimensions, can prevent column failure.
- Quality Control: Quality control during the manufacturing process can help to identify and eliminate material defects before they become a problem.
- Maintenance: Regular maintenance can prevent corrosion and other environmental factors that can lead to column failure.
- Inspection: Regular inspection of columns can detect cracks, corrosion, or other defects that could lead to failure.
- Foundation Design: Proper foundation design can prevent foundation failure, which can lead to column failure.
Also, read: Development Length for Reinforcement Bar: Anchorage Length & Lap Length with Formula
FAQs:
1: What is column failure?
Ans: Column failure occurs when a column is no longer able to support the load it was designed to carry, resulting in collapse or deformation.
2: What are the causes of column failure?
Ans: The causes of failure can include excessive load, poor design, material defects, corrosion, fatigue, construction errors, foundation failure, and environmental factors.
3: What are the types of column failure?
Ans: The types of column failure include buckling failure, crushing failure, shear failure, fatigue failure, corrosion failure, overloading failure, and foundation failure.
4: What are the signs of column failure?
Ans: Signs of column failure can include cracking, deformation, leaning, or settlement.
5: How can column failure be prevented?
Ans: Column failure can be prevented through proper design, quality control, maintenance, inspection, and foundation design.
References:
- Indian Standard. (2000). Code of Practice for Plain and Reinforced Concrete (IS 456:2000) (4th ed.). Bureau of Indian Standard (BIS).
- Duggal S. K. (2014). Limit State Design of Steel Structures. McGraw Hill Education (India) Private Limited. New Delhi
- Chandra, R. (2013). Reinforced Concrete Structure (Limit State Design) (1st ed.). Standard Book House, Rajsons Publications Pvt. Ltd.
- Discoveries, E. (2023, October 26). Types of column failure, reasons, and prevention of column failure. Engineering Discoveries. https://engineeringdiscoveries.com/types-of-column-failure-reasons-and-prevention-of-column-failure/
![]()